단순 연결 리스트란 ?
이전 2. Linked List (연결 리스트) 포스트에서 설명된 내용을 기반으로 설명하겠습니다.
연결리스트는 데이터 간에 '연결'되어 있다고 했는데, 연결은 아래와 같이 두 가지 방법이 있다.
- A 에서 B로 갈 때(단방향), A ㅡ> B 또는 B ㅡ> A
- A 에서 B로 가고 B에서도 A로 갈 수 있을 때(양방향), A <ㅡ> B 또는 A ㅡ B
단순 연결리스트는 이 중, 단방향에 대한 정보를 사용하는 것이 단순 연결리스트이다.
대신, 주의할 점이 있다. A가 시작점, B가 종점인 경우에는 B에서 A로 갈 수 없다.
즉, 순환이 발생하지 않는다는 점이다.
A ㅡ> B ㅡ> A ㅡ > B ( X )
A ㅡ> B ㅡ> 끝 ( O )
단순 연결리스트는 이게 끝이다.
그럼, 주로 어떻게 사용되고 어떻게 구현하면 되는지를 알아보려고 포스트를 작성한다.
C++ STL로는 forward_list가 있다.
사용처
우리가 특정 지역에 자유 여행을 가게 된다면 우리가 계획 한 여행 코스가 있을 것이다.
상황극을 한 번 해보자.
음.. 오늘은 공부를 하고 노래를 하기로 했지?
아니다.. 근데 노래보다 피시가 더 재밌을 것 같아 피시를 먼저하고 노래를 하자.
이 때, 단순 연결 리스트를 사용한다면 공부 ㅡ> 노래 에서 공부 ㅡ> 피시 ㅡ> 노래로 표현 할 수 있다..
이미 우리가 공부를 했는데 아 공부 대신 밥을 먹을걸 ;;; 이라면서 이미 했던 공부를 밥을 먹은 것으로 속일 수 있는가?
이렇게 과거에 지난 일은 신경 쓸 필요가 없는 데이터의 흐름을 표현할 때는 단순 연결 리스트를 사용하는 것이 좋다.
이 외에도 일상생활에서 사용되는 경우를 한 번 생각해보면 좋은 시간이 될 것 같다.
그리고 해시, 스택, 큐 등 자료구조에서도 단순 연결 리스트가 사용된다. (이것은 나중에 다루겠음.)
구현 ( C++ )
Linked List의 Node 헤더 생성
캡슐화, 정보은닉, 템플릿, 헤더 중복 고려
#pragma once
template <typename T>
class Node {
public:
Node(T data);
T getData() const;
Node* getNext() const;
template <typename U>
friend class SinglyLinkedList;
void setNext(Node* node);
private:
T data;
Node* next;
};
template <typename T>
Node<T>::Node(T data) : data(data), next(nullptr) {}
template <typename T>
T Node<T>::getData() const {
return data;
}
template <typename T>
Node<T>* Node<T>::getNext() const {
return next;
}
template <typename T>
void Node<T>::setData(T data) {
this->data = data;
}
template <typename T>
void Node<T>::setNext(Node* node) {
next = node;
}
노드 헤더를 이용한 Singly Linked List 헤더 생성
#pragma once
#include "SinglyLinkedListNode.h"
template <typename T>
class SinglyLinkedList {
public:
SinglyLinkedList();
class iterator {
public:
iterator(Node<T>* node);
T operator*() const;
iterator& operator++();
bool operator!=(const iterator& other) const;
private:
Node<T>* it;
};
iterator begin();
iterator end();
iterator find(const T& value);
void insert(const T& value);
void erase(const T& value);
int getSize();
private:
Node<T>* head;
int size;
};
template <typename T>
SinglyLinkedList<T>::iterator::iterator(Node<T>* node) : it(node) {}
template <typename T>
T SinglyLinkedList<T>::iterator::operator*() const {
return it->getData();
}
template <typename T>
typename SinglyLinkedList<T>::iterator& SinglyLinkedList<T>::iterator::operator++() {
it = it->getNext();
return *this;
}
template <typename T>
bool SinglyLinkedList<T>::iterator::operator!=(const iterator& other) const {
return it != other.it;
}
template <typename T>
SinglyLinkedList<T>::SinglyLinkedList() : head(nullptr), size(0) {}
template <typename T>
typename SinglyLinkedList<T>::iterator SinglyLinkedList<T>::begin() {
return iterator(head);
}
template <typename T>
typename SinglyLinkedList<T>::iterator SinglyLinkedList<T>::end() {
return iterator(nullptr);
}
template <typename T>
typename SinglyLinkedList<T>::iterator SinglyLinkedList<T>::find(const T& value) {
Node<T>* node = head;
while (node != nullptr && node->getData() != value) {
node = node->getNext();
}
return iterator(node);
}
template <typename T>
void SinglyLinkedList<T>::insert(const T& value) {
Node<T>* newNode = new Node<T>(value);
if (head == nullptr) {
head = newNode;
} else {
Node<T>* node = head;
while (node->getNext() != nullptr) {
node = node->getNext();
}
node->setNext(newNode);
}
size++;
}
template <typename T>
void SinglyLinkedList<T>::erase(const T& value) {
Node<T>* node = head;
Node<T>* prev = nullptr;
while (node != nullptr && node->getData() != value) {
prev = node;
node = node->getNext();
}
if (node != nullptr) {
if (prev != nullptr) {
prev->setNext(node->getNext());
} else {
head = node->getNext();
}
delete node;
size--;
}
}
template <typename T>
int SinglyLinkedList<T>::getSize() {
return size;
}
Custom SinglyLinkedList를 활용한 사용 예제
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include "SinglyLinkedList.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "======= My Custom Singly Linked List =======\n";
SinglyLinkedList<string> customList;
customList.insert("My");
customList.insert("Custom");
customList.insert("Singly");
customList.insert("Linked");
customList.insert("List");
for (auto it = customList.begin(); it != customList.end(); ++it) {
cout << *it << ' ';
}
cout << "\n";
cout << "length of list before delete : " << customList.getSize() << '\n';
auto it = customList.find("Custom");
if (it != customList.end()) {
cout << "delete : " << *it << '\n';
customList.erase(*it);
}
for (auto it = customList.begin(); it != customList.end(); ++it) {
cout << *it << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
cout << "customList's size = " << customList.getSize();
return 0;
}
아니 코드 줄이 왜 안맞는거지??;;;
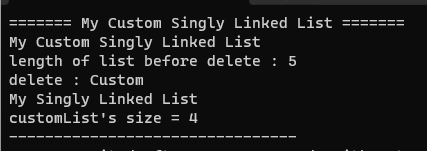
실행결과
Github
jihwankim128/datastructure
Contribute to jihwankim128/datastructure development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
물론 좀 더 쉽게 작성할 수는 있지만, STL 흉내를 내보고 싶었다 ^^!
STL 참고 자료
https://cplusplus.com/reference/forward_list/forward_list/
https://cplusplus.com/reference/forward_list/forward_list/
difference_typea signed integral type, identical to: iterator_traits ::difference_type usually the same as ptrdiff_t
cplusplus.com
생각해보니까 STL에 사용되는 메서드를 그대로 구현하면 되구나...
STL에는 없는 find 같은 것을 구현해봤는데 뭐.. 좋은 경험이었다. 앞으로는 STL 따라하기 ㅎㅎ
다음 포스트부터는 STL에 사용되는 메서드를 그대로 구현해보기. ( 물론 적당한 양만 )
'알고리즘 > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 6. STL 사용하기 - std::list (0) | 2024.02.11 |
|---|---|
| 5. 원형 연결 리스트 (Circular Linked List) (1) | 2024.02.10 |
| 4. STL 따라잡기 - 이중 연결 리스트 (Doubly Linked List) 구현 (0) | 2024.02.07 |
| 2. 연결 리스트 (Linked List) (1) | 2024.02.04 |
| 1. 자료구조란? (2) | 2024.01.26 |

